What is pulse oximetry and how does it work?
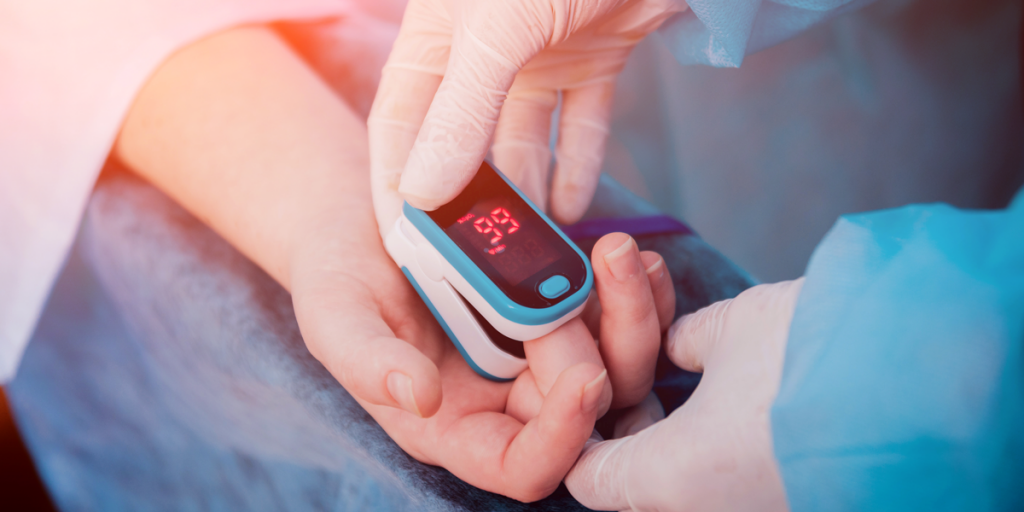
What is pulse oximetry and how does it work? Pulse oximetry is a noninvasive method that enables rapid measurement of the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin in arterial blood.1 It can rapidly detect changes in oxygen saturation, thus providing an early warning of dangerous hypoxemia.2, 3 How it works: A pulse oximeter (like the Nonin GO2) shines light at two wavelengths—red and infrared—through a…
Read More10 Tips to Selecting the Right Professional Finger Pulse Oximeter
How do you know which finger pulse oximeter* is right for your use? 10 Tips to Selecting the Right Professional Finger Pulse Oximeter: How accurate is the oximeter and are the accuracy claims backed by evidence, e.g., published papers? Will the oximeter work on a variety of patients, and does your oximeter specifically list accuracy for patients with low perfusion or dark skin…
Read MoreHow to access enteral systems without opening lines
Maintain a closed system helping keep you and your patients safe. Enteral valve technology allows access to enteral systems without opening the lines, protecting healthcare workers from exposure to gastric fluids, mucus membrane secretion, and bloodborne pathogens, such as HIV and Hepatitis C. The Lopez Valve® features clinically-proven stopcock technology that maintains a closed system throughout enteral feeding, drug…
Read MoreHow does your cath lab handle radiation protection?
How does your cath lab handle radiation protection for physicians and staff? Minimally invasive interventional procedures lower costs and risks for patients. Ironically, physicians put themselves at greater risk and pay a personal high price in radiation exposure multiple times every day. ALL Fluoro-guided procedures produce scatter radiationSome interventional procedures result in significantly more scatter radiation than…
Read MoreHow to Protect from Scatter Radiation during Vascular Surgery
ALL Fluoro-guided Procedures Produce Scatter Radiation Some interventional procedures result in significantly more scatter radiation than others. Differentiating factors include: complexity of procedure, total fluoro time, size of patient, and operator proximity to the primary beam/image intensifier. Minimally invasive interventional procedures lower costs and risks for patients. Ironically, physicians put themselves at greater risk and paya…
Read MoreDo you have EtCO2 monitoring when performing procedural sedation
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) “Standards for Basic Anesthetic Monitoring” recommends monitoring for the presence of exhaled carbon dioxide during procedures where the patient is sedated.* The ASA standard states: “During moderate or deep sedation the adequacy of ventilationshall be evaluated by continual observation of qualitative clinical signsand monitoring for the presence of exhaled…
Read More